In 2013, the National Association of Corrosion Engineers revealed a startling fact: corrosion cost the world a staggering 2.5 trillion USD.
Rust is a form of corrosion, showing up on everything from your garage door to your car and even the framework of your home. Repairing the damage costs range from a minor 20 or 30 bucks to maybe thousands, making it a real headache for homeowners and industries. So, what exactly is steel rust, and how can you avoid it while keeping your expenses as low as possible?
Table of Contents
What is Steel Rust and How Does it Happen?
Picture that reddish, flaky coating of iron oxide on steel surfaces – that’s rust. It’s a result of a chemical reaction between iron, oxygen, and moisture. Think of it like a science experiment you might’ve seen in school, involving an anode (usually zinc) and a cathode (typically copper) in the presence of a conductive medium also called a galvanic cell.
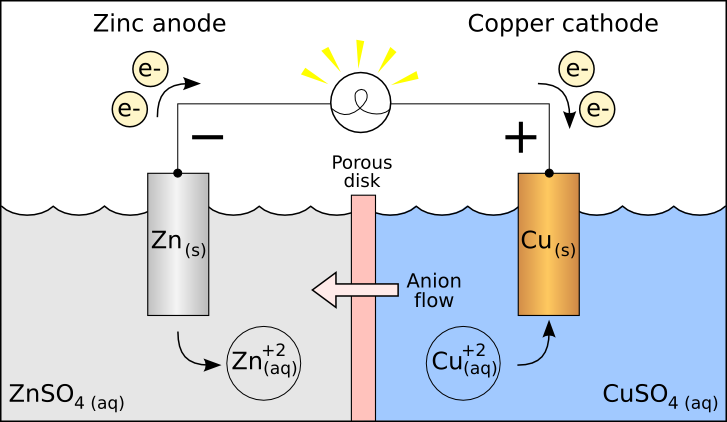
As steel is an alloy which means there is a set of metallic elements mixed to provide more strength or resistance to corrosion, the cathode and anode are within the steel alloy all you need is a salt-bridge (medium) and oxygen for rust to start forming
Rust: Impact and Cost
Rust can affect our lives in many ways. Understanding the impact and the cost involved is crucial:
- Structural Damage: Rust can weaken important structure components, which compromises buildings’ safety and maintenance costs
- Equipment damages: In industries, rust can mess up machinery and equipment, leading to downtime, costly repairs, or replacement.
- Aesthetic Nightmares: Rust on surfaces like vehicles, fences, and appliances is plain ugly and can even hurt their resale value.
- Health Hazards: In some cases, rust can contaminate water sources, posing health risks for people and animals.
- Economic and environmental Loss: The financial impact of corrosion is large, affecting both individuals and economies. Preventing rust can save significant amounts in maintenance and repair costs.
How to Protect Steel from Rust
There are several effective methods to protect steel:

- Galvanizing: Named after the inventor of the galvanic cell, Luigi Galvani, this one comes in two forms:
- Hot-Dip Galvanizing: Dunking steel into a zinc solution bath gives it a nice protective zinc coat. The perks? It’s like zinc is sacrificing itself to protect the steel. There’s some impressive abrasion and erosion resistance and a solid bond between the coat and steel. Plus, it ensures an even coat all over.
- Cold Galvanizing: This one’s all about painting an epoxy-based zinc-rich coat. Give it two coats with an 8-hour breather in between. Cold galvanizing is flexible and perfect for on-site action and post-construction.
- Alkyd and Iron Oxide Primers: Not as super-effective as galvanizing, but these paints form a barrier that keeps the rust away. Any paint that shields steel from humidity and oxygen can offer some protection.
- Rust Converter: Here’s the magic potion: a chemical solution, mostly a tannic acid blend. It works wonders by turning rust into a protective layer that stops corrosion. Best part? You can just spray it on rusty steel, even those hard-to-reach spots.
Comparison of Rust Prevention Methods
| Rust Prevention Method | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot-Dip Galvanizing | Steel is immersed in a zinc solution bath | Excellent protection, even coating | Requires outsourcing for treatment |
| Cold Galvanizing | Epoxy-based zinc-rich paint applied | On-site application, post-construction use | Requires frequent inspection and maintenance |
| Alkyd and Iron Oxide Primers | Paint that isolates steel from humidity and oxygen | Simple application, some protection | Less effective than galvanizing |
| Rust Converter | Chemical solution that converts rust into a protective layer | Effective for hard-to-reach spots | Less suitable for large surfaces |
Taking Action: What to Do About Rust on Steel
Spot even a speck of rust on your steel? Don’t wait – act now! Rust is like that one guest who just won’t leave; it needs to be removed. Grab some emery paper or a steel brush and scrub away the rust. Do it as many times as needed to make sure you’ve evicted every bit of rust. Then, reapply the protective coating to maintain a barrier against future corrosion.
And here’s a tip: don’t expose steel to salt bridges like soil and water or acidic substances. making it a slow but sure transformation from steel to rust.
Advanced Methods of Rust Prevention
While the methods above are rock-solid, technology brings us even fancier tools for rust prevention:
- Nano-Coatings: Apply these protective coatings to steel surfaces, creating an invisible forcefield that keeps moisture and oxygen off the surface preventing rust formation
- Cathodic Protection Systems: These systems use electric current to protect steel. There are two primary methods: sacrificial anodes and impressed current systems. Sacrificial anodes are made of materials like zinc and aluminum, which corrode in place of steel. Impressed current systems use an external power source to drive current into the steel, preventing corrosion.
- VCI (Volatile Corrosion Inhibitors) Technology: inhibitors are materials with specific physical properties. they include a substance or material to prevent further escalation. Thus, Volatile Corrosion Inhibitors release vapor-phase corrosion inhibitors, forming a protective layer on steel that rust can’t breach.
Rust-Resistant Steel Alloys
We’ve got steel alloys that stand strong against corrosion. These alloys have special elements mixed in, like chromium and nickel, that create a protective layer on the steel’s surface.
- Stainless Steel: It’s got chromium that makes a thin, self-healing oxide layer on the surface.
- Galvanized Steel: is coated with a layer of zinc, which provides robust protection against rust. This zinc coating is especially effective in harsh environments.
- Corten Steel: Also known as weathering steel is an alloy that consists of copper, chromium, and other elements, it forms a protective layer of rust. this unique rusted appearance is often used in architectural designs.
- Cast iron Rust occurs less on cast iron due to slags and impurities in wrought iron, providing resistance to corrosion
| Steel Alloy | Composition | Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Chromium, nickel | Forms a protective rust layer, a unique appearance | Kitchen appliances, medical devices, architectural applications |
| Galvanized Steel | Zinc coating | Excellent rust protection, ideal for harsh environments | Building materials, automotive parts |
| Corten Steel | Alloy steel | Forms a protective rust layer, unique appearance | Architectural designs, outdoor sculptures |
| Cast Iron | Iron, carbon, silicon | Naturally resistant to rust and corrosion | Engine blocks, cookware, pipes, outdoor decor |

Innovative Approaches to Rust Prevention
Innovation drives the development of rust prevention methods. emerging techniques include:
- Biological Corrosion Prevention: Researchers are exploring the use of bacteria and other microorganisms to inhibit rust. These microorganisms form protective films on steel surfaces.
- Graphene Coatings: It’s ultra-thin and tough. It forms a solid barrier against corrosion, scratches, and other environmental factors.
The Importance of Routine Maintenance
Preventing rust is an ongoing process. Routine maintenance is essential to ensure protective coatings and methods remain effective. Here are some key maintenance tasks:
- Regular Check-Ups: Inspect steel surfaces from time to time for any signs of rust or coating damage.
- Touch-Up Time: If you spot areas where the protective coatings are chipped or showing signs of wear, give them a touch-up.
- Clean and Shine: Clean steel surfaces to get rid of dirt or salt.
- Cathodic Protection System Checks: If you’ve got a cathodic protection system in place track its performance.
- Watch the Environment: Environmental conditions, like humidity, temperature, and exposure to chemicals, can affect rust. Keep an eye on these factors during your maintenance routine.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Rust Prevention
Real-world examples illustrate the significance of rust prevention:
- The Golden Gate Bridge: This iconic bridge, faces off against a corrosive marine environment. It’s rust-free thanks to high-performance coatings, regular inspections, and maintenance.
- Oil and Gas Industry: Pipelines, storage tanks, and offshore structures in the oil and gas industry tackle harsh conditions with advanced coatings and cathodic protection systems. They kept steel corrosion-free and the oil flowing.

The Role of Government Regulations
Regulations set the standards for materials, coatings, and maintenance practices. They’re there to make sure our infrastructure and industrial equipment are safe and sound. Follow these rules to avoid penalties and keep the public safe.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Investing in Rust Prevention
Rust prevention might seem like a splurge, but it’s all about the long game. Investing in these measures can save you a bundle over the life of a structure or piece of equipment. Well-maintained, rust-free stuff lasts longer and needs fewer repairs.
Conclusion
Rust in steel is a real nuisance with far-reaching consequences. It affects our structures, industries, and daily lives. Understanding its causes, prevention methods, and the importance of maintenance is key. Use the right material for your purpose. combine both traditional and innovative rust prevention methods and stay updated on emerging technologies.

