A construction site is a busy world, teeming with activity, as the outcome project is always challenging. These sites are in a constant state of change, adapting to the evolving:
- Safety Requirements
- Environmental concerns, diverse workforce
- Material sourcing and mobilization
- Waste and contamination management.
Table of Contents
Preparing for the Project
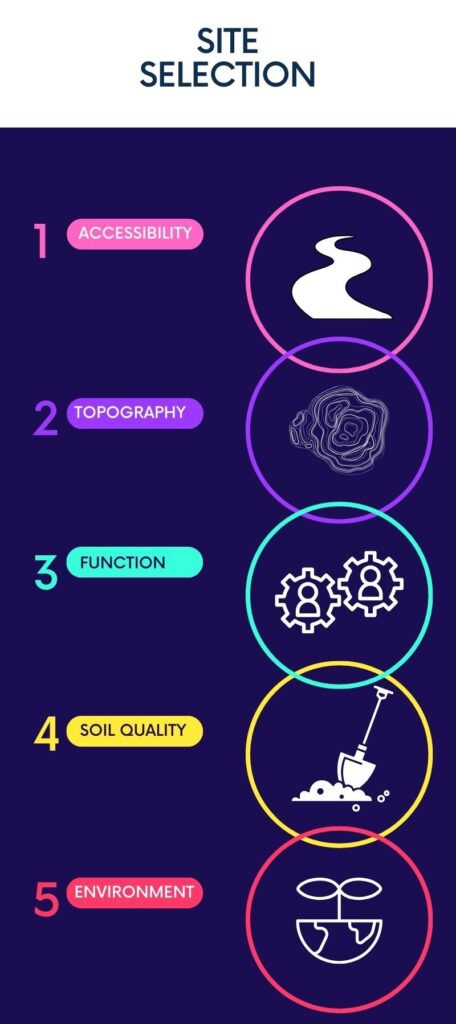
Construction Site Selection
The Selected construction site must service the business case of the project and stakeholders’ desire, for that you may take into consideration the following factors.
- Accessibility
- Site Topography
- Project function
- soil quality
- Environmental impact assessments: In recent times, environmental responsibility has taken center stage. Building on sensitive land or near endangered species habitats can pose significant challenges. for instance, the construction of wind farms needs consideration to environmental impacts on birds(USA EIA).
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
- Occupational Health and Safety: In the United States, OSHA sets and enforces safety and health regulations for the construction industry.
- Building Codes and Standards
- Environmental Regulations
- Zoning and Land-Use Regulations
- Permitting and Licensing
- Contractual Agreements
- Labor Laws
- Quality Control and Inspection
- Accessibility Standards
- Anti-Corruption Due Diligence and Ethics

non-compliance with standards and regulations can lead to project delays and financial penalties,
Site Preparation (facilitating works)
- Site survey: produce site layouts to ensure ease of maneuver during construction.
- Identify earthwork
- Land clearing
- Setting up access roads
- Safety, and informative signs
- Installing fences, temporary facilities, and infrastructure
- Mobilization plan
Site Safety and Maintenance
Safety Policies and Procedures:
Safety is an ongoing process. regular inspections and audits to maintain a safe working environment. Training and retraining of workers to keep them updated with safety protocols.

- Conduct a Safety Assessment: Begin by assessing the specific risks associated. Identify potential hazards, both common and project-specific.
- Develop a Safety Policy and Procedures: high-level documents that set the tone for safety within your organization. procedures should be practical and easy to follow. HSE induction and regular meetings that Involve Employees. provide incentives and recognition. training and communication are essential.
- Safety Equipment and Gear: Supply workers with the necessary equipment and gear. protective equipment (PPE), such as hard hats, safety glasses, and high-visibility vests.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping: Maintain thorough records of training, inspections, etc.
- Hazard and fire fighting systems.
- surveillance and AI: Cameras are getting cheaper and Artificial intelligence is getting smarter. Deploying AI Survaliance systems can help secure the site, avoid conflicts, and monitor safety
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
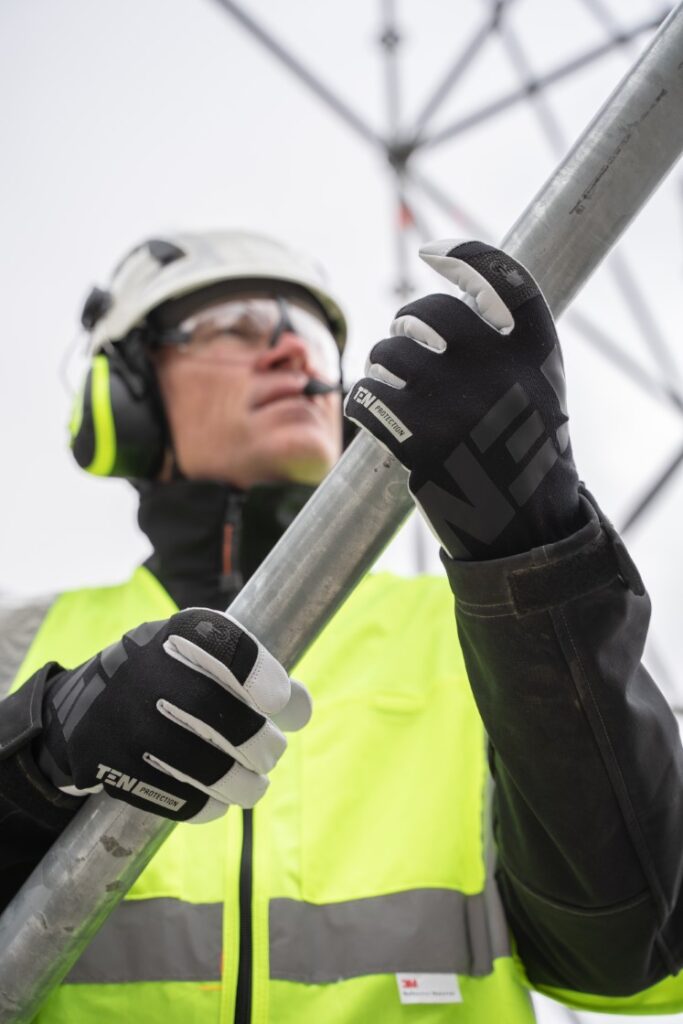

The types of PPE required on construction sites vary based on the work.
- Hard Hats, Safety Goggles, gloves, and Steel-Toed Boots.
- High-Visibility Vests.
- Fall Protection Equipment: Safety Harnesses, belts, lines, and nets.
- Respirators and Dust Masks.
The COVID-19 pandemic brought a new dimension to the use of PPE on construction sites. Workers needed protection from the virus by using face masks, and enhanced sanitation measures.
Site Clean-Up

Once the construction is completed. Clean and restore the site post-construction. mitigate any environmental impact. you also need to flush any piping systems, especially water supply systems.
Material Quality Control and Inspection
The choice of materials impacts the quality, durability, and aesthetics of a project.
- Material specifications and selection: dig deep into material specifications and functions to ensure you have the right product for the right job. material selection and installation should meet the required standards and workmanship.use proper storage methods and areas.
- Proper Site Layout: The site layout includes designated areas for material storage. strategically locate materials to reduce handling and transportation distances.
- Efficient use of materials: by reducing waste and recycling.
- Inventory Management: to track the quantity, condition, and location of materials. This helps in avoiding overstocking, understocking, or material deterioration.
Environmental and Social Considerations
In 2021, the United States spent 1.6 trillion dollars. this huge industry can easily shift the market and impact the social landscape.
Waste Management
30% of materials delivered on-site will turn to waste. ironically, also 30% of the global waste is produced by construction and demolition. therefore construction sites should adopt sustainability and recycling practices like:

- Prefabrication and Modular Construction: Off-site construction methods reduce waste and improve construction efficiency.
- Waste Sorting Stations: On-site waste sorting stations and waste management apps make recycling more efficient.
- Lean Construction: focus on optimizing processes, whether it’s material waste or inefficient workflows.
- Renewable Energy Integration: solar panels and wind turbines reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower carbon emissions.
- Certification and Rating Systems: LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) or BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method) ensure sustainable construction practices.
- Life-Cycle Assessments (LCA): evaluating the building’s environmental impact over its entire life cycle.
- Passive Design Strategies: utilizing passive design principles like natural ventilation, daylighting, thermal mass, and Stormwater and Wastewater Management.
- Adaptive Reuse: Transform existing buildings and structures for new purposes instead of demolishing them.
- Employment Opportunities & Skill Development: Construction projects offer job opportunities and develop valuable skills and expertise.
Communication and Collaboration
Team Collaboration
Integration is key to project success, which requires communication channels, to align stakeholders and all construction disciplines to the same objectives and timeline.
Building Information Modeling (BIM) Revolution:
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a technological innovation that has revolutionized collaboration. It is a shared 3D model of the project improving communication, reducing errors, and conflicts,
Challenges and Problem-Solving
- Overcoming Unforeseen Delays: Delays are common challenges in construction. Unexpected issues, like weather conditions or supply chain disruptions, affect the project’s timeline.
- Adaptability: Construction projects rarely go exactly as planned. adapt and respond to changing circumstances.
For expert guidance on managing your construction projects, visit our Construction Management page




